- September 26, 2025 3:14 pm
- by Aruthra
- September 26, 2025 3:14 pm
- by Aruthra
The term parser frequently appears in computer science, especially in programming, compilers, and natural language processing. It plays a foundational role in how systems interpret and process input, whether in the form of code, commands, or even human language. However, for those who are new to this domain, the concept of a parser might initially appear complex.
This blog aims to provide a clear and comprehensive explanation of what a parser is, why it is important, the various types of parsers, and where they are commonly used.
A parser is a software component that takes input data (usually in the form of text) and analyzes it according to a set of grammatical rules. Its main job is to break down this input into a structure that a machine can understand and process further.
In most contexts, parsers are used in conjunction with grammars, which define the rules that the input must follow. These grammars can describe programming languages, data formats (like JSON or XML), or even spoken language.
Parsers serve as the bridge between human-generated input and computer understanding. Here are a few reasons why parsers are essential:
While the term "parser" may seem singular, it generally consists of two main stages:
This is the first stage where the input is divided into meaningful units called tokens. These tokens can be words, numbers, symbols, or keywords, depending on the context. This phase is sometimes handled by a separate component known as a lexer or scanner.
In this stage, the parser examines the sequence of tokens to determine if they follow the predefined grammatical rules. If they do, the parser generates a structured representation of the input, often in the form of a syntax tree. If not, it flags a syntax error.
Together, these stages allow the parser to understand the structure and organization of the input data.
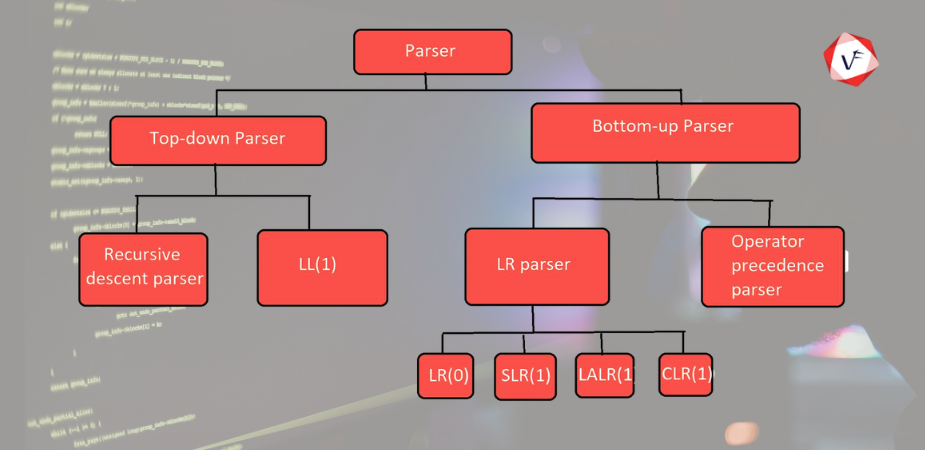
Parsers can be categorized based on how they analyze the input. The most common classifications are top-down parsers and bottom-up parsers.
Top-down parsers start from the highest-level rule (also known as the start symbol) and try to derive the input string by applying grammar rules in a forward direction.
Top-down parsers are typically easier to implement and understand but may not handle complex grammatical structures as effectively as bottom-up parsers.
Bottom-up parsers start from the input symbols and try to reduce them to the start symbol of the grammar by reversing the derivation process.
Bottom-up parsers are more complex to implement but can process more sophisticated and ambiguous grammar rules.
Parsers are used in a wide range of systems, often without the user being aware of them. Here are a few real-world examples:
One of the main functions of a parser is to detect and report errors. When the input does not match the grammar rules, the parser generates an error message.
Common parsing errors include:
Effective parsers not only detect errors but also attempt to recover from them and provide meaningful feedback.
Once the input is successfully parsed, the parser typically produces a tree-like structure:
These trees are then used by the compiler or interpreter to generate output, optimize performance, or execute the input commands.
Various tools and libraries are available for building parsers, depending on the programming language and use case. Some popular ones include:
These tools help developers avoid writing parsers from scratch by providing ready-to-use frameworks for defining grammars and generating parse trees.
Understanding what a parser is and how it works is fundamental to grasping the inner workings of many software systems. While the concept may seem technical at first, it becomes much more approachable when broken down into its basic components and practical applications.
Parsers help ensure that human input—whether code, data, or spoken language—is structured in a way that machines can understand. They are, in many ways, the unsung heroes of modern computing, quietly working behind the scenes to enable communication between people and machines.
As technology continues to evolve and become more reliant on automated understanding, the role of parsers will only become more significant. Whether you are a software developer, data analyst, or someone simply curious about how computers interpret input, a foundational knowledge of parsers is a valuable asset.
A parser checks syntax and converts code into structured data (syntax tree) for further compilation.
Top-down parsers (recursive descent, predictive) and bottom-up parsers (shift-reduce, LR parser).
Web browsers (HTML parser), databases (SQL parser), and NLP tools (sentence parsing).
Guaranteed Response within One Business Day!
5G/6G + Edge + AI: How Ultra‑Fast Connectivity Is Enabling New Business Models

Building Software That Thinks for Itself: Agentic AI in Modern SaaS

Open-Weight vs Closed Models: How Startups Should Choose Their AI Stack
What Is OpenClaw? The Open-Source AI Agent That Runs on Your Hardware in 2026

10 Best AI Coding Assistant Tools in 2026 (From a Developer Who's Tried Them All)